In an unprecedented and thrilling scientific breakthrough, NASA’s Mars rover has discovered a fossil-like rock on the surface of the Red Planet, suggesting the existence of ancient life on Mars. This groundbreaking discovery has ignited global excitement and could potentially answer one of humanity’s most profound questions: Are we alone in the universe?
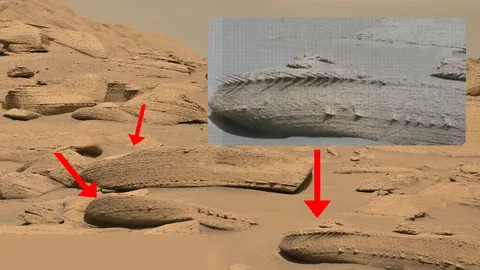
The journey to this monumental discovery began with NASA’s Perseverance rover, which has been exploring Mars’ Jezero Crater. This area, once home to a lake, has long been a focal point for scientists searching for signs of past life. The rover’s sophisticated imaging and analysis tools recently identified a rock formation that bore a striking resemblance to fossilized bones found on Earth.

Upon closer examination, the rock revealed structures and patterns remarkably similar to those of ancient fossils. Detailed spectroscopic analysis indicated the presence of complex organic compounds, bolstering the hypothesis that these formations are indeed fossilized remains. While further analysis is required, the initial findings are compelling, providing strong evidence that microbial life once existed on Mars.
This discovery marks a pivotal moment in the field of astrobiology. The presence of fossil-like rocks on Mars suggests that the planet may have once harbored conditions suitable for life. This supports the theory that life can arise in diverse environments, potentially extending beyond Earth. The implications are staggering, opening new avenues for the search for extraterrestrial life and expanding our understanding of life’s resilience.
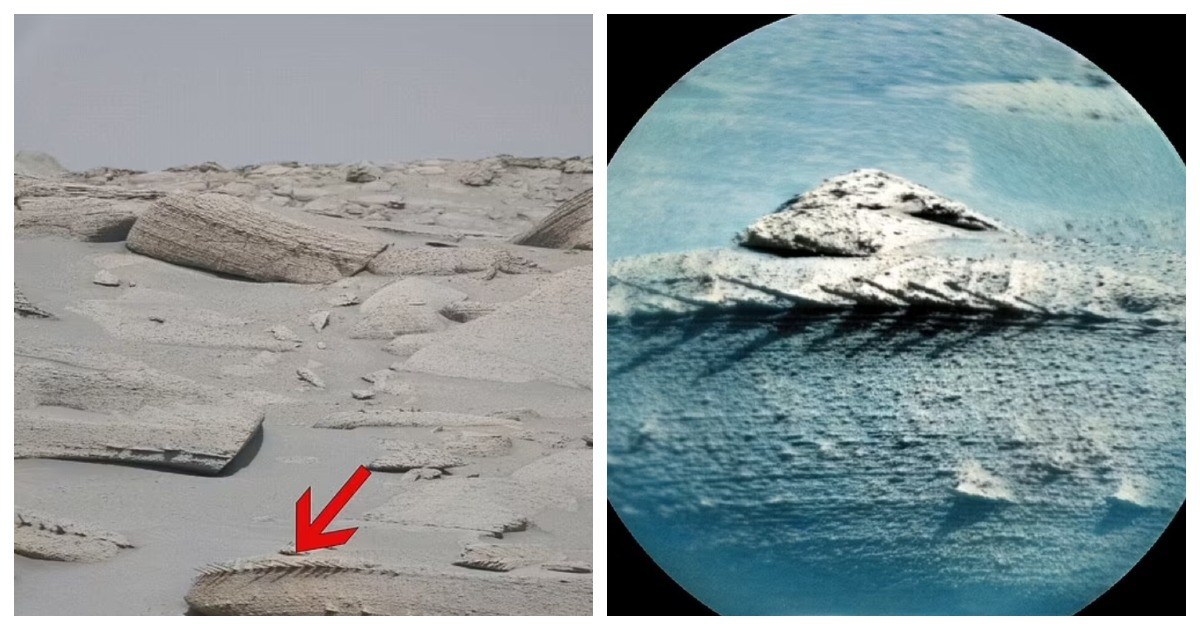

The geological context of the discovery provides further insights into Mars’ ancient environment. The Jezero Crater, with its preserved river delta and lake sediments, offers a snapshot of Mars’ wetter and potentially habitable past. The fossil-like rock hints at a time when Mars had liquid water, a thicker atmosphere, and conditions conducive to life.
NASA’s scientific team is now focused on conducting more in-depth analyses of the rock sample. Plans are underway to drill into the formation and retrieve samples for potential return to Earth. These samples could provide definitive evidence of ancient Martian life and offer unprecedented insights into the planet’s geological and biological history.
The discovery has galvanized the global scientific community, prompting collaborations and discussions across international space agencies and research institutions. The European Space Agency (ESA) and other organizations are keen to contribute to the ongoing analysis and future missions aimed at exploring Mars’ potential for life.
Beyond the scientific realm, this discovery has captured the public’s imagination. The notion of finding evidence of ancient life on another planet resonates deeply, inspiring wonder and curiosity about the universe. It serves as a reminder of the importance of space exploration and the profound questions it seeks to answer.
As we stand on the brink of potentially confirming extraterrestrial life, we must also consider the ethical and philosophical implications. How will this discovery reshape our understanding of life and our place in the cosmos? What responsibilities do we have in preserving and studying these ancient Martian relics? These questions will guide our approach to space exploration in the years to come.
The discovery of a fossil-like rock on Mars’ surface is a groundbreaking milestone in our quest to understand the universe. It provides compelling evidence that ancient life once existed on the Red Planet, opening new chapters in the story of life’s origins and existence beyond Earth. As we continue to explore Mars and other celestial bodies, we move closer to unraveling the mysteries of the cosmos and our place within it.




