The origins of humanity have long intrigued scholars and scientists alike, driving archaeological endeavors to piece together our evolutionary journey from apes to Homo sapiens. Yet, significant gaps in our understanding persisted until a groundbreaking discovery emerged, potentially illuminating a crucial chapter in human history. Experts have unearthed a 3.8 million-year-old skull that promises to reshape our understanding of human evolution, shedding new light on our ancestral roots.
The site of Warano Mills, located approximately 300 miles from Ethiopia’s capital, Addis Ababa, initially appeared unremarkable. However, beneath its surface lay a profound archaeological treasure waiting to be uncovered. In 2016, a goat herder named Ali Bareno stumbled upon a jawbone protruding from the earth, igniting a series of events that would captivate the scientific community.
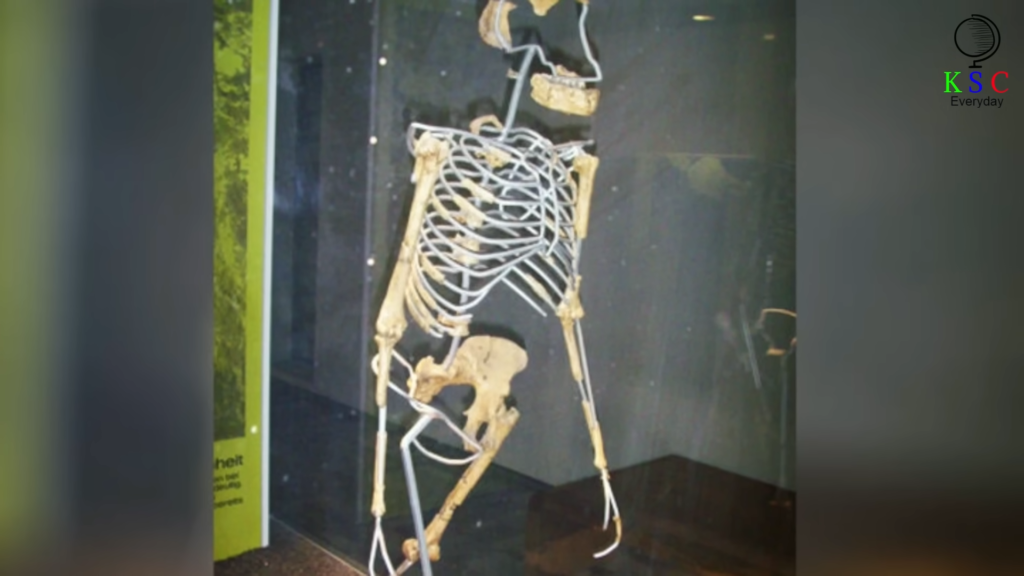

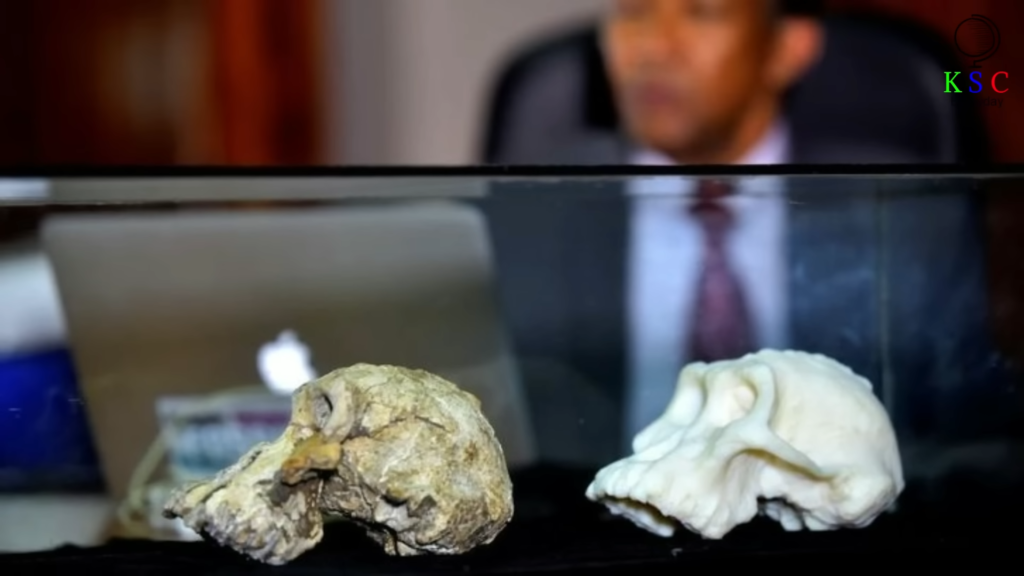
Upon examination, experts realized the significance of Bareno’s discovery: it was a maxilla belonging to the Australopithecus anamensis species, a precursor to humanity. This find marked the first tangible evidence of Australopithecus anamensis’s existence, filling a critical void in paleoanthropology.
The subsequent excavation led by Dr. Johannas Hail Salassie yielded astonishing results. After a rigorous 16-hour dig, researchers uncovered more fragments, including the rest of the skull. The euphoria among the team was palpable as they grasped the magnitude of their discovery – a pivotal moment in understanding human evolution.

Named “MRD,” the skull provided unprecedented insights into the Australopithecus anamensis species. Its features, a blend of primitive and derived traits, challenged conventional theories and hinted at a complex evolutionary narrative. Through meticulous analysis and comparison with other specimens, scientists pieced together MRD’s story, revealing clues about its diet, behavior, and habitat.
One of the most remarkable revelations came from comparing MRD with another fossil, the “Bodo” frontal piece. This comparison reshaped our understanding of human evolution, suggesting that Australopithecus anamensis and Australopithecus afarensis, including the famous “Lucy,” coexisted for a significant period.
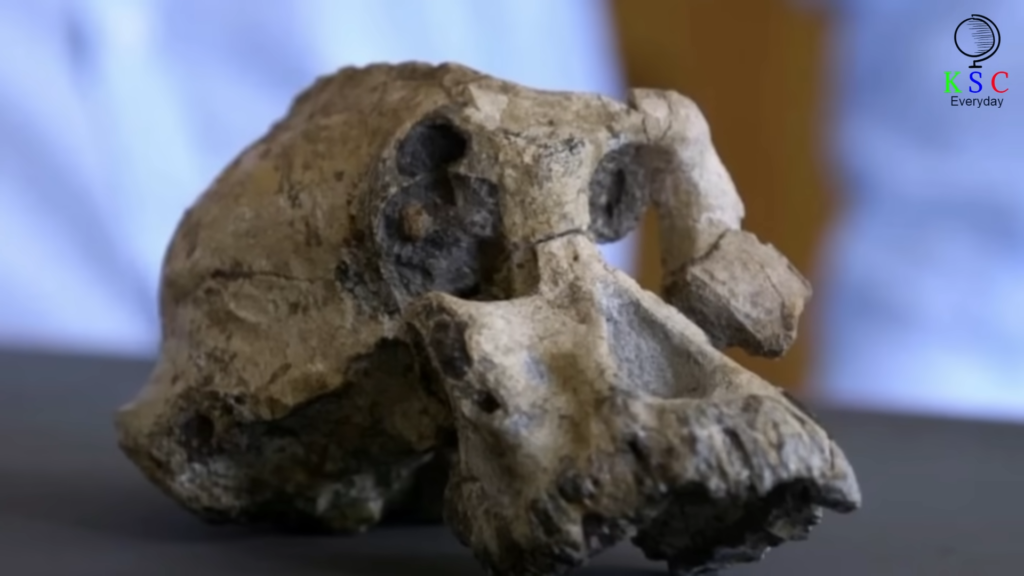

The implications of this discovery are profound, sparking debates and prompting further exploration. While some remain cautious, calling for more evidence, the MRD skull represents a transformative moment in our quest to unravel the mysteries of human evolution.
As researchers continue their investigations, one thing is certain – the MRD skull has opened a new chapter in our collective journey, inviting us to reconsider our place in the vast tapestry of evolution. With each new revelation, the story of humanity grows richer, more complex, and undeniably captivating.
Thank you for watching, and don’t forget to like and subscribe for more updates on this groundbreaking discovery.




